-
Introduction
-
Getting Started
- First Login
- Dashboard
- Navigation
- User Profile
-
Administration
- User Management
- Tenant Settings
- Activity Log
-
Risk Management
- Risks
- Risk Assessments
- Threats
- Incidents
- Findings
-
Control Management
- Controls
- Control Objectives
- Effectiveness Reports
-
Tasks
- Task Management
-
Compliance
- References
- Requirements
- Requirement Groups
- Evidence
-
Assessments
- Baselines
- Challenges
-
Organization & Assets
- Legal Entities
- Locations
- Teams
- Persons
- IT Assets
- Information Assets
- Physical Assets
- Products
- Processes
- Capabilities
- Third Parties
- Engagements
- Scope Groups
-
Blueprints
- Blueprints
-
Structures
- Standards
- Domains
- Categories
- Projects
- Assurances
-
Compliance ID
- Overview
- General Settings
- VUCA Score Sharing
- Control Sharing
- Requirement Sharing
- Assurance Sharing
- News & FAQ
- Access Management
- Subscriber Management
- The Public ID Page
Introduction
VUCA Score
Introduction
Your VUCA score is a real-time health indicator for your GRC program. Unlike compliance checklists that show binary pass/fail status, the VUCA score reflects the quality, currency, and completeness of your risk and compliance posture across four dimensions: Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity.
The score updates automatically as you work. Address overdue risks, complete assessments, assign owners, attach evidence. Each action that improves your compliance posture lowers your VUCA score. Each gap or delay increases it.
This page explains how the score works, what drives each dimension, and how to improve your organizational health.
Understanding Your Score
Navigate to VUCA in the sidebar to see your current score and detailed breakdown.
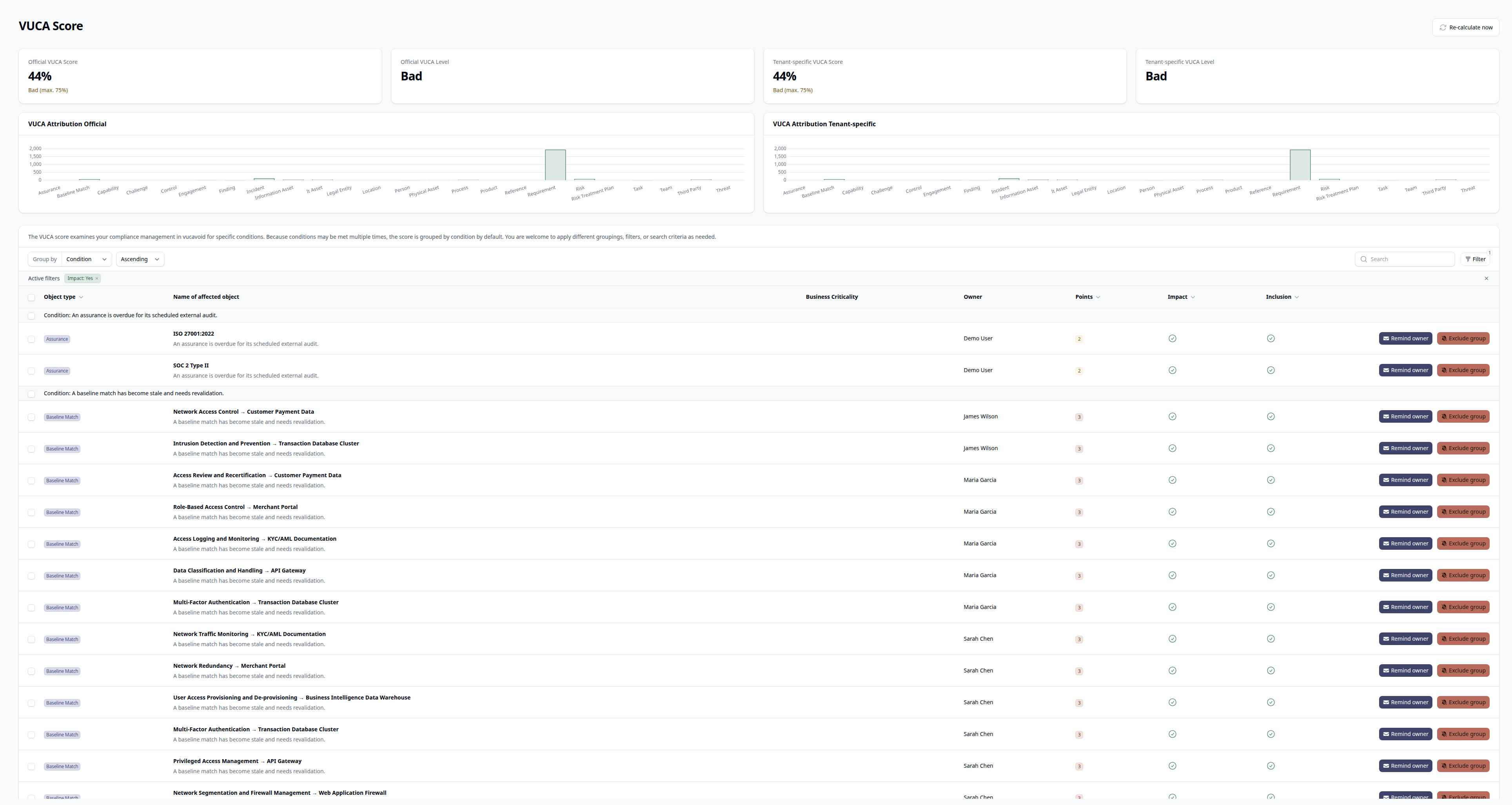
The VUCA page displays four key metrics:
| Metric | What It Shows |
|---|---|
| VUCA Score | Your official score as a percentage (0-100%+) |
| VUCA Level | Qualitative rating based on score thresholds |
| Tenant-Specific Score | Your customized score after excluding generators |
| Tenant-Specific Level | Qualitative rating for your customized score |
Both scores use the same calculation logic. The difference is that the tenant-specific score lets you exclude certain generators that don't apply to your organization.
Score Levels
Your score maps to a qualitative level that indicates overall compliance health:
| Score Range | Level | Color | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-5% | Perfect | Green | Exceptional. All tracked items current, owned, and addressed. |
| 6-15% | Very Good | Green | Strong posture. Minor gaps that don't indicate systemic issues. |
| 16-25% | Good | Green | Healthy program. Some areas need attention but fundamentals are solid. |
| 26-40% | Mediocre | Blue | Warning zone. Multiple gaps accumulating. Prioritize remediation. |
| 41-75% | Bad | Orange | Significant issues. Compliance posture degraded. Urgent attention needed. |
| 76%+ | Uncontrolled | Red | Critical. Program has lost control. Immediate intervention required. |
Score Interpretation
A score of 0% doesn't mean you have no risks or compliance obligations. It means everything you're tracking is current, assigned, and addressed. A healthy, mature GRC program should aim for Good or better (≤25%).
New organizations typically start with higher scores as they build their GRC program. The score naturally decreases as you complete initial setup: assigning owners, performing first assessments, attaching controls to requirements.
The Four Dimensions
Each dimension captures a different aspect of organizational uncertainty. Understanding what drives each helps you prioritize improvements.
Volatility (V)
Volatility measures rapid changes and instability in your compliance posture. High volatility means things are changing faster than you're addressing them.
What increases Volatility:
- Overdue risk treatment deadlines
- Risks with high current severity (High/Medium assessment levels)
- Overdue control effectiveness reports
- Findings in Initial status (unaddressed)
- Active incidents (especially with high priority or PII impact)
- Requirements not fully complied
- Controls pending implementation for extended periods
- Paused controls (especially those linked to high-severity risks)
- Treatment plans stuck or overdue
- Expiring or expired engagements
- Poor external audit results
- High-risk third-party assessments
How to reduce Volatility:
- Address overdue deadlines promptly
- Complete risk treatments on schedule
- Maintain control effectiveness reporting cadence
- Remediate findings quickly
- Resolve incidents and link them to risks for future prevention
Uncertainty (U)
Uncertainty measures unknowns and gaps in your compliance data. High uncertainty means you don't have a clear picture of your actual posture.
What increases Uncertainty:
- Risks without any assessment
- Risk assessments older than 12 months
- Objects (assets, processes, etc.) without assigned owners
- Objects without capability assignments
- Capabilities without owners
- Processes without documentation
- Overdue tasks
- References without requirements attached
- References not assigned to any objects
- Risks without controls
- Risks without treatment plans
- Controls with missing or ineffective effectiveness reports
- Controls missing evidence in effectiveness reports
- Controls with overdue reviews
- Requirements not assigned to any objects
- Third parties without assessments
- Third parties with overdue reviews
- Stale baseline matches
- Threats not linked to risks
- Incidents not linked to risks
- External audits without reports
How to reduce Uncertainty:
- Perform initial assessments on all risks
- Keep assessments current (at least annually)
- Assign owners to every object
- Link objects to capabilities
- Document processes
- Complete tasks before due dates
- Attach requirements to references
- Link controls to risks they mitigate
- Create treatment plans for active risks
- Maintain evidence in effectiveness reports
Complexity (C)
Complexity measures intricate relationships and operational difficulty. High complexity indicates structural issues that make compliance harder to manage.
What increases Complexity:
- Objects without business criticality assigned
- References without domains or categories
- Treatment plans stuck in Initial/InProgress status for extended periods
- Active incidents (contribute to multiple dimensions)
- Requirements with only partial fulfillment
- High-risk third-party assessments
- Engagements expiring or expired
- Overdue assurance audits
- Poor external audit results
- Threats stuck in Initial/InProgress status
How to reduce Complexity:
- Assign business criticality to all objects
- Categorize references with domains and categories
- Resolve stuck treatment plans (complete or close them)
- Move requirements from partial to full fulfillment
- Address high-risk third parties
- Manage engagement lifecycles proactively
Ambiguity (A)
Ambiguity measures lack of clarity and insufficient information. High ambiguity means accountability and purpose are unclear.
What increases Ambiguity:
- Objects without capability assignments
- Objects without business criticality
- Objects without owners
- Findings marked as "not remediated"
- Overdue tasks
- References without requirements
- References not assigned to objects
- Risks without treatment plans
- Capabilities without owners
- Processes without documentation
- Controls with missing effectiveness reports
- Third parties without assessments or overdue reviews
- External audits without reports
- Threats not linked to risks
- Incidents not linked to risks
- Stale baseline matches
How to reduce Ambiguity:
- Assign clear ownership to everything
- Define business criticality and capabilities
- Document processes
- Link records to related entities
- Resolve or document findings explicitly
- Address baseline match staleness
Score Calculation
The VUCA score is calculated from approximately 45 generators, each examining a specific aspect of your GRC program.
How Generators Work
Each generator:
- Queries a specific model type (risks, controls, requirements, etc.)
- Evaluates each record against specific criteria
- Assigns a score based on severity (typically 0-6 points per record)
- Contributes to one or more VUCA dimensions
For example, the RiskOverdueGenerator:
- Finds all active risks with Overdue status
- Assigns 4 points to each
- Tags those points as Volatility
Criticality Weighting
Most generators weight scores by criticality:
| Criticality | Typical Weight |
|---|---|
| Essential | Highest (3-6 points) |
| High | High (2-4 points) |
| Medium | Medium (0.5-3 points) |
| Low | Low or zero (0-2 points) |
An overdue task with Urgent priority impacts your score more than one with Low priority. An unowned Essential asset impacts more than an unowned Low-criticality asset.
Minimum Thresholds
Generators only activate when you have sufficient data. An organization with 3 risks won't be penalized for risk-related gaps the same way an organization with 100 risks would be. This prevents artificially high scores during initial setup.
Score Aggregation
The final percentage is calculated as:
VUCA Score = (Sum of all generator scores / Sum of all maximum scores) × 100
The maximum score represents the theoretical worst case for each generator. Your actual score divided by this maximum gives the percentage.
Two Score Types
vucavoid calculates two scores:
Official VUCA Score
The standard score using all applicable generators. This represents your objective compliance posture and is useful for:
- Benchmarking against industry standards
- Reporting to auditors and stakeholders
- Tracking improvement over time
Tenant-Specific Score
A customized score where you can exclude certain generators. Use this when:
- Specific generators don't apply to your organization (e.g., third-party generators if you don't use vendors)
- You want to focus on specific improvement areas
- Certain compliance requirements are out of scope for your certification
Excluding Generators
Excluding generators removes their impact from your tenant-specific score but doesn't fix the underlying issues. Use exclusions thoughtfully. The official score always reflects your complete posture.
Exclusions are tracked with audit trail. The system records who excluded each generator and when, ensuring accountability for scope decisions.
Managing Your Score
Viewing Score Details
The VUCA page shows a detailed breakdown of every record contributing to your score.
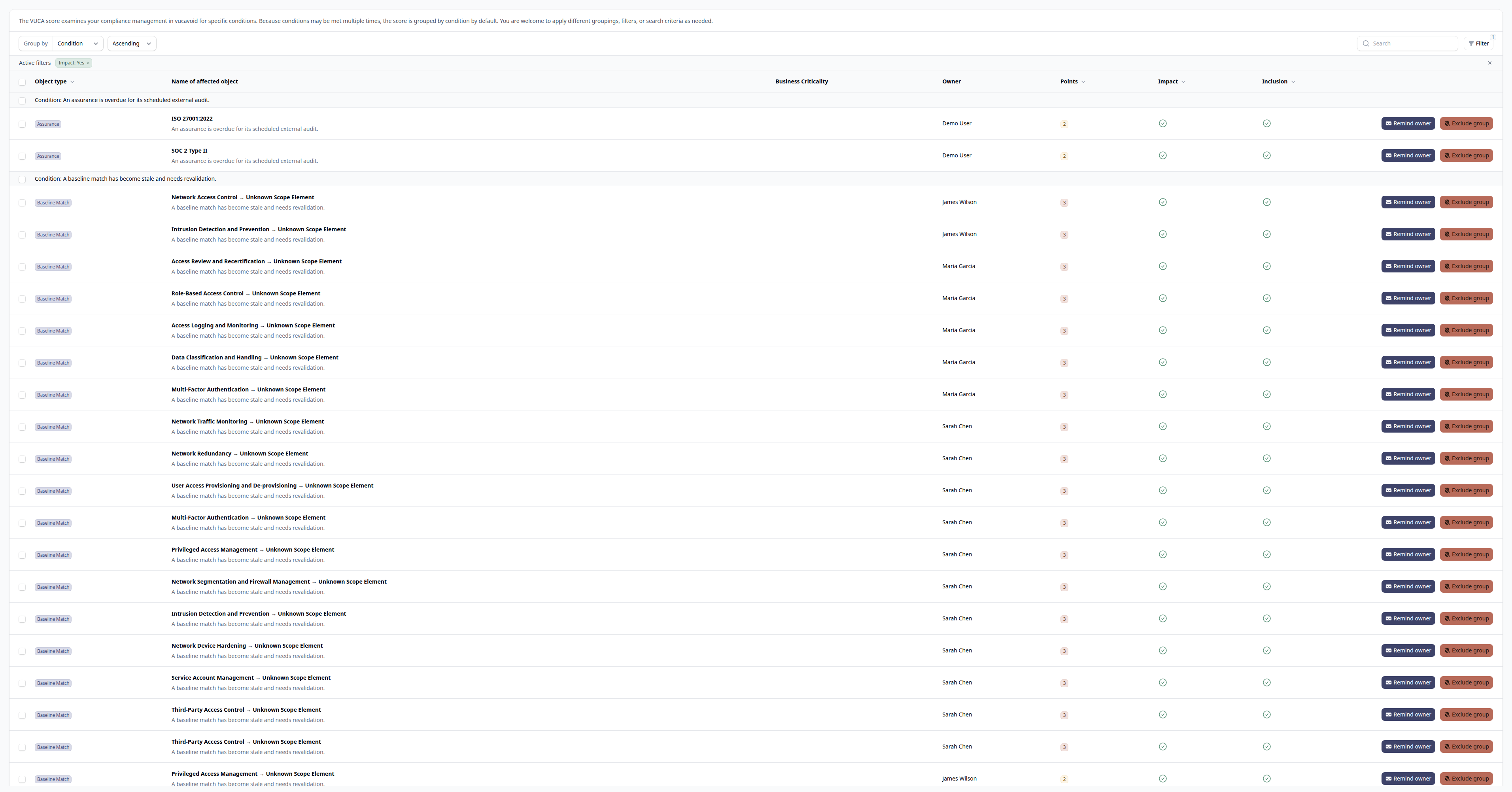
You can:
- Filter by impacting items — See only records that increase your score
- Filter by owner — Review a specific person's impact on the score
- Filter by criticality — Focus on high-impact items
- Filter by model type — See all risks, all controls, etc.
- Group by generator — Understand which checks are failing
Taking Action
Each item in the VUCA breakdown links to its source record. Click through to:
- Assign missing owners
- Update overdue assessments
- Complete pending tasks
- Attach evidence to controls
- Resolve stuck items
Reminding Owners
For items with assigned owners, use the Remind Owner action to send a notification highlighting the item's impact on the VUCA score. This is useful for delegating remediation without micromanaging.
Excluding/Including Generators
For the tenant-specific score, you can exclude entire generator categories:
- Find any item from the generator you want to exclude
- Click Exclude to remove that generator from your tenant-specific score
- The official score remains unchanged
To re-include a previously excluded generator, click Include.
Score Trends
The VUCA page displays trend charts showing how your score has changed over time. Trends help you:
- Verify improvement efforts are working
- Spot degradation before it becomes critical
- Correlate score changes with organizational events
- Demonstrate progress to stakeholders
Scores are calculated periodically (typically every 30 minutes). You can also manually trigger a recalculation using the Generate VUCA Score action.
Best Practices
Start With Ownership
The fastest way to reduce your initial score is assigning owners. Objects without owners contribute to Uncertainty and Ambiguity. A single pass assigning owners often drops the score significantly.
Prioritize by Criticality
Focus on Essential and High criticality items first. These contribute more to your score and represent your most important assets. Low-criticality items can wait.
Maintain Cadence
Steady, consistent work beats sporadic catch-up sessions. Review your VUCA score weekly. Address a few items each day rather than letting them accumulate.
Don't Chase Zero
A Perfect score (0-5%) is achievable but shouldn't be the primary goal. Good (≤25%) indicates a healthy program. Obsessing over zero can lead to gaming the system rather than genuine improvement.
Stale Programs Kill Scores
The most common cause of high VUCA scores is staleness. Not missing data, but outdated data. Assessments from two years ago. Deadlines that passed six months back. Evidence that hasn't been refreshed.
Schedule regular reviews. Monthly for high-criticality items, quarterly for the rest. A current, modest program scores better than a comprehensive but stale one.
Related Resources
- Key Concepts — Understanding the VUCA methodology and compliance architecture
- Dashboard — Overview of the main dashboard including VUCA widgets
- Risks — Risk management and how risks affect the VUCA score
- Controls — Control management and effectiveness reporting
- Baselines — Baseline monitoring and stale match handling
- Tasks — Task management and overdue handling
